How ERP-Integrated EDI Reduces Supply Chain Errors
By Brian Eckenrod on
When EDI runs in a silo from your ERP, errors sneak in—mismatched POs, duplicate invoices, missed ASNs, delayed payments. ERP-integrated EDI eliminates manual re-keying, syncs master data, and automates validations so your team spends less time chasing fixes and more time moving orders.
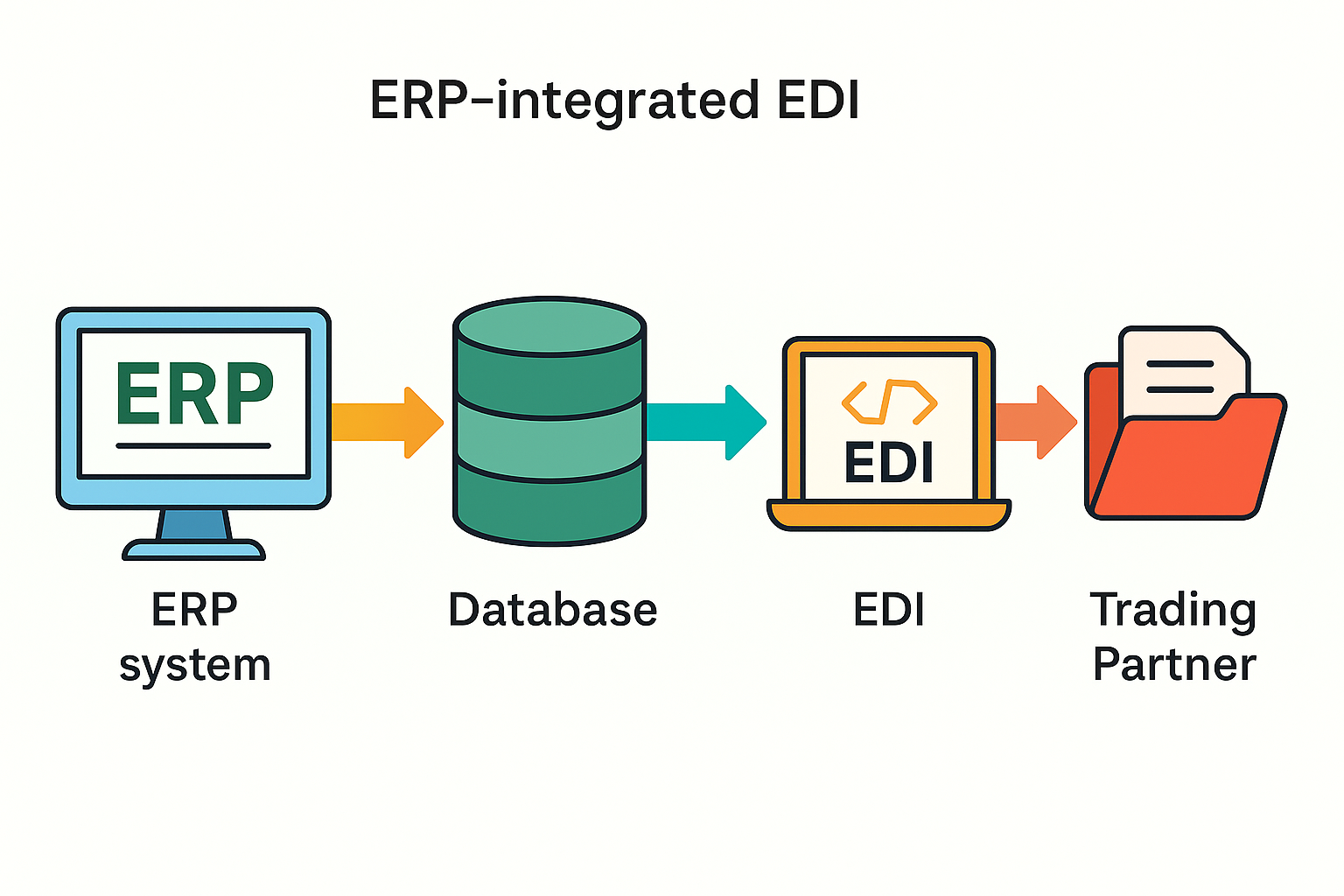
What Is ERP-Integrated EDI?
ERP-integrated EDI is a direct, automated connection between your ERP (items, pricing, partners, orders) and your EDI transaction flows. Instead of exporting/importing files or keying data by hand, records move bi-directionally in real time or near-real time. The result is fewer touchpoints, fewer errors, and faster cycles.
How Integration Reduces Errors
Most supply-chain mistakes trace back to manual entry and mismatched data. Integration prevents these issues at the source:
- PO ↔ Invoice agreement: Quantities, prices, and units are validated automatically.
- Catalog integrity: Item codes, pack sizes, GTINs, and UOMs inherit from ERP masters.
- Partner-specific rules: Retailer mandates are enforced before transmission.
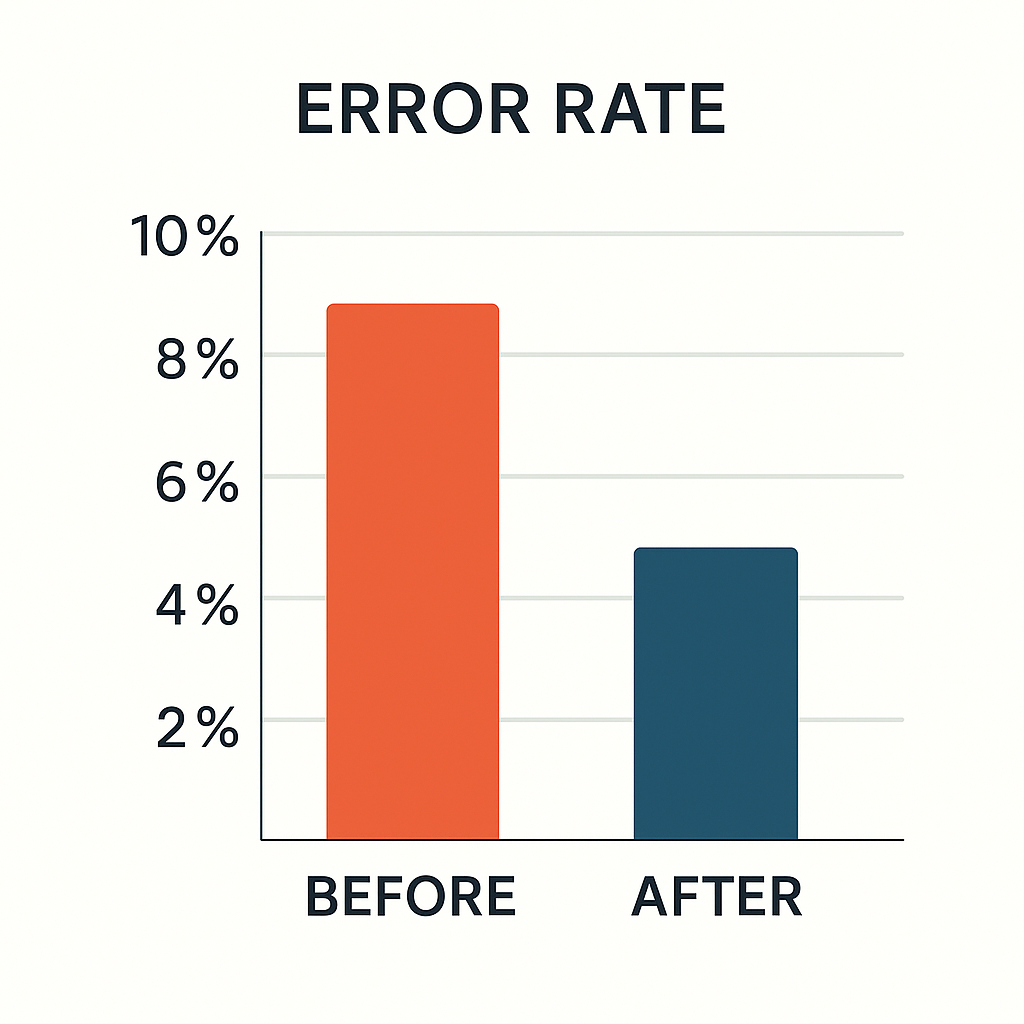
Why it matters: Fewer exceptions and chargebacks, faster dispute resolution, and measurably lower error rates across the order-to-cash cycle.
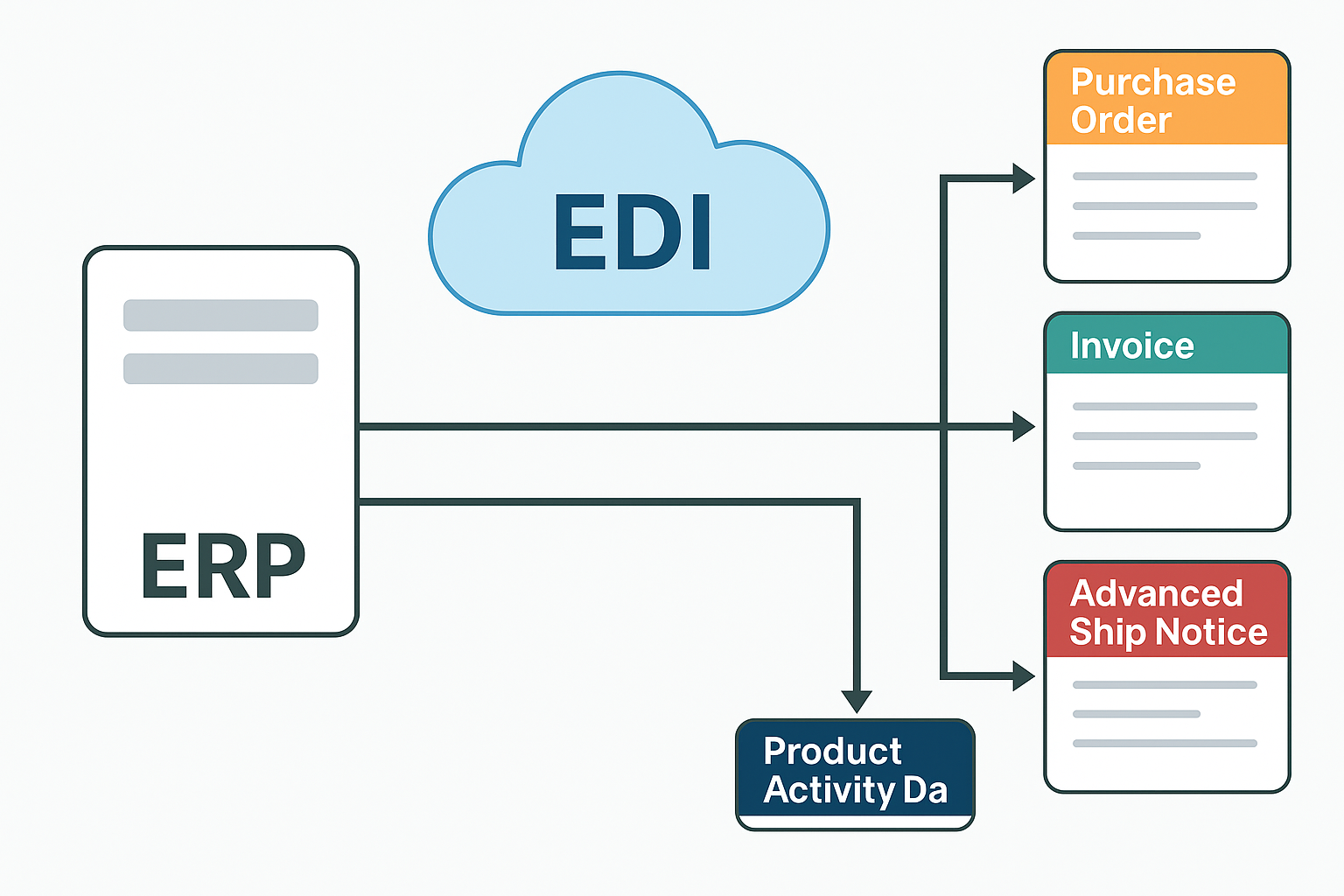
Documents That Benefit Most
Automation delivers outsized impact on high-volume, high-touch documents. With ERP-integrated EDI, these flow cleanly without re-keying:
- 850 Purchase Orders → validated to item/pricing master data
- 855/997 Acks → confirmation and audit trail back to ERP
- 856 Advanced Ship Notices → packing detail validated to orders
- 810 Invoices → price/qty checks minimize disputes
- 852 Product Activity → demand and inventory signals integrated to planning
Compliance, Security & Visibility
Integrated EDI keeps you aligned to GS1/X12, enforces partner-specific rules, and routes acknowledgements for audit. Add 24/7 monitoring and real-time exception alerts, and your team sees issues before partners do—shrinking cycle times and protecting OTIF performance.
- Standards: GS1 / ANSI X12 consistency reduces mapping friction.
- Security: Encrypted transport, role-based access, and audit trails.
- Visibility: Exceptions push back into ERP queues for rapid resolution.
Implementation Pattern & Timeline
Most mid-market teams roll out in phases: start with PO/ASN/Invoice for top partners, then expand. A typical pattern: discovery & mapping (2–4 weeks), pilot connections (2–6 weeks), scale out (ongoing). With a managed provider, onboarding runs in parallel so growth doesn’t stall on hiring.
Conclusion
ERP-integrated EDI removes the root causes of supply-chain errors—manual entry and data mismatch—while improving compliance and speed. If you’re ready to shrink exceptions, reduce chargebacks, and accelerate partner onboarding, integrating EDI to ERP is the most reliable path forward.
Next step: Talk with our team about an integration plan tailored to your ERP and trading partners.
Comments are closed